Part 5B. Ground Effect Materials
1. If we’re going to make this look like Yellowstone, we need to change the Western Desert ground to look more like a series of volcanic deposits. Go to the Ground Editor Material page.
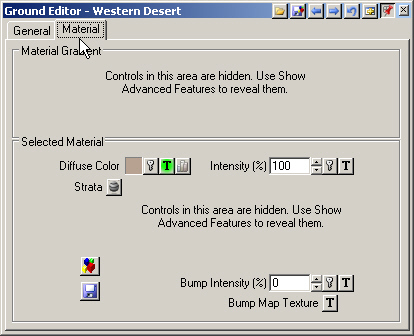
2. Select Show Advanced Features on the titlebar to reveal the Material Gradient.
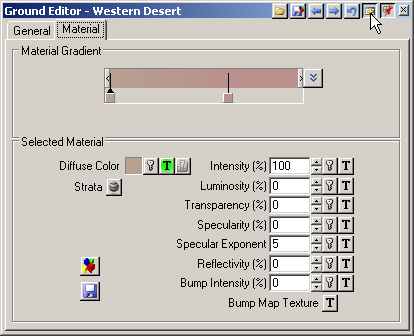
3. Click Show Material Controls at the right end of the gradient to access Material Gradient controls.
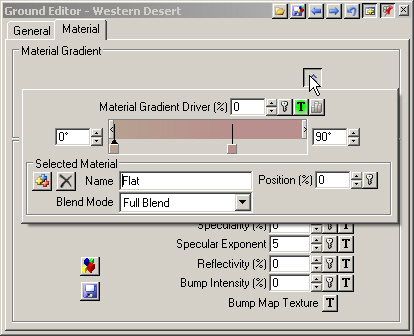
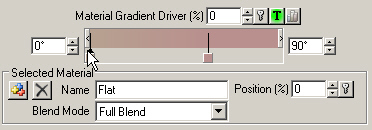
4. This Ground Effect is made up of 2 Materials, Flat and Steep, controlled by a Material Gradient. The left color pin is the Flat Material and the right pin is Steep.
5. What controls the gradient? Click the Material Gradient Driver Texture Operations button and Edit Texture.
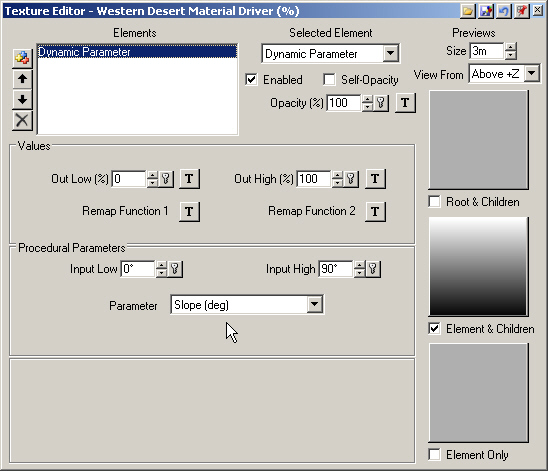
6. The texture is a Dynamic Parameter, one that changes depending on a project parameter. In this case, Slope is the Parameter controlling the texture. The slope goes from an Input Low of 0° to an Input High of 90°, which are the same numbers that appear at each end of the Material Gradient. This texture is using terrain slope to place the Flat and Steep Materials. Close the editor.
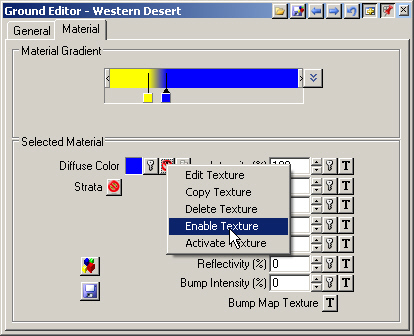
7. To see all the Flat Material properties, make its pin active and Show Material Controls to hide the controls.
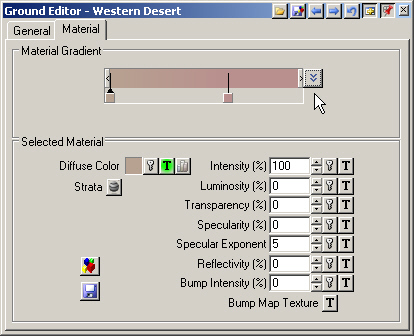
8. The Selected Material section shows that the Flat Material has a Diffuse Color texture. When there’s a texture, it supersedes the color well. When the texture has transparency, the color well color will show through.
9. Select the Diffuse Color well to open its Color Editor.Change the color to yellow: Red 255, Green 255, and Blue 0. You can also pick a color from one of the Swatches, or create a Swatch of your own and add it to the Components\Image\Color Swatch folder.
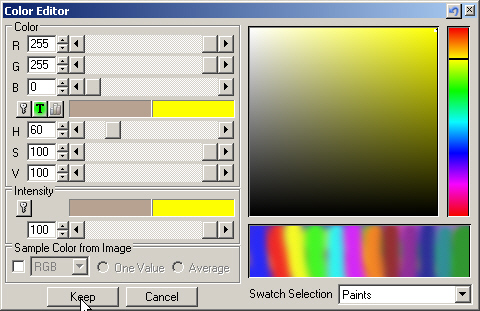
10. Keep the color and Disable the Diffuse Color texture.
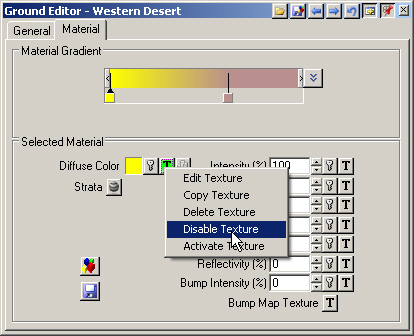
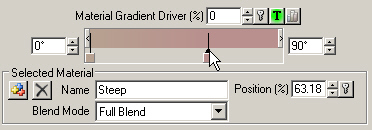
11. Click the right pin in the Material Gradient to make the Steep Material active.
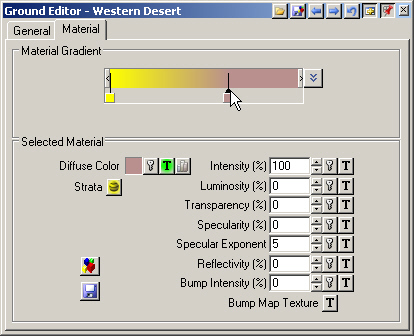
12. Change its color to blue: Red 0, Green 0, and Blue 255.
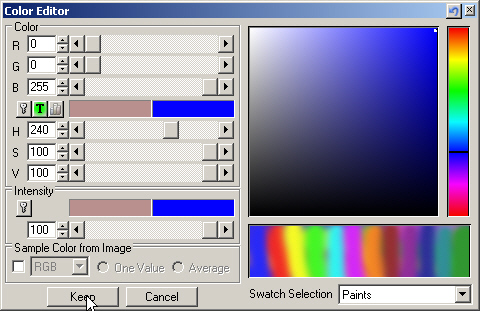
13. Keep the color and Disable the Diffuse Color texture.
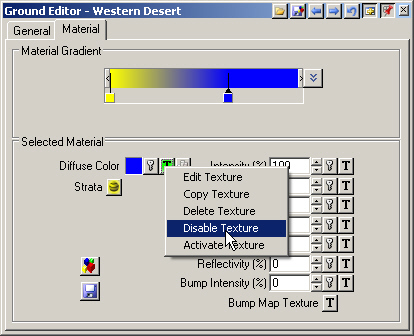
14. Disable the Strata channel.
15. Save the project and render a preview. Simple colors are a good way to evaluate Ground Effect and Ecosystem coverage.
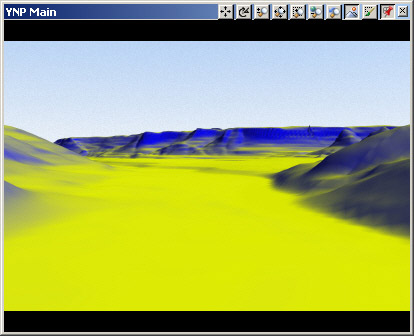
16. The blue Steep Material needs to render farther down the slope. Show Diagnostic Data and click and drag at the base of the foreground hills to see the slope values. They range from about 20° to 30°.
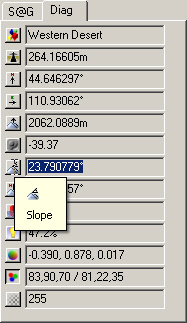
17. Show Material Controls for the Material Gradient. We’d like a sharper transition between Flat and Steep Materials somewhere around 20°. Select the yellow Flat pin and change its Position to 20%.
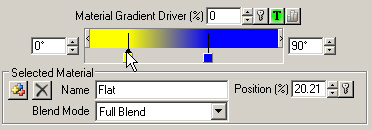
18. Select the blue Steep pin and enter a Position value of 30%. Flat Material will give way to Steep Material between 20% and 30% of 90°, or between 18° and 27°.
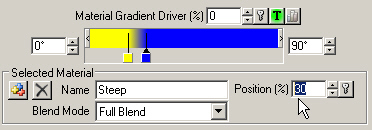
19. Hide the Material Controls. Save the project and render a preview.
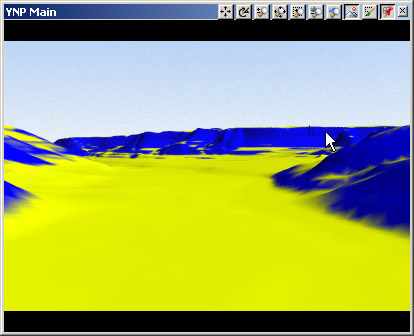
20. That’s the transition we’re looking for. Enable the Diffuse Color Texture and Strata channels. Select the Flat Material pin in the Material Gradient and enable its Diffuse Color Texture.
21. Save the project and render a preview.